Abstract
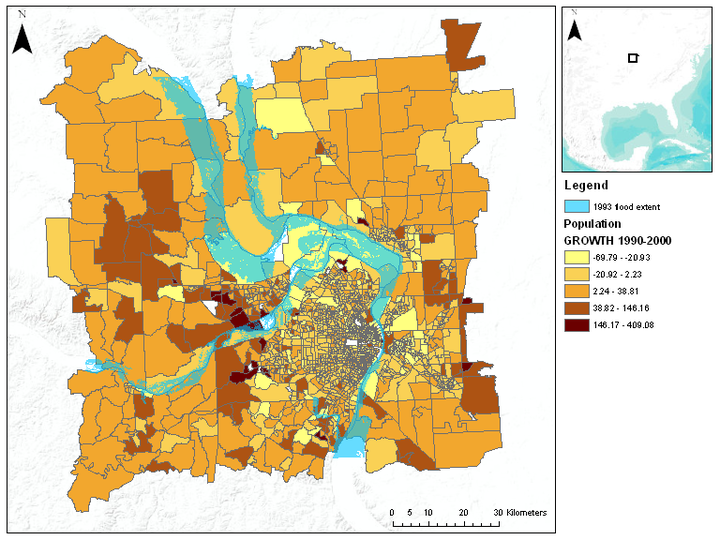
Human societies have learnt to cope with flood risks in several ways, the most prominent ways being engineering solutions and adaptive measures. However, from a more sustainable point of view, it can be argued that societies should avoid or at least minimize urban developments in floodplain areas. While many scientists have studied the impact of human activities on flood risk, only a few studies have investigated the opposite relationships, i.e. the impacts of past flood events on floodplain development. In this study, we make an initial attempt to understand the impact of the occurrence of flood disasters on the spatial distribution of population dynamics in floodplain areas. Two different methodologies are used to uncover this relationship, a large-scale study for the USA and a case-study analysis of the 1993 Mississippi flood. The large-scale analysis is performed at county level scale for the whole of the USA and indicates a positive relationship between property damage due to flood events and population growth. The case-study analysis examines a reach of the Mississippi river and the territory, which was affected by flooding in 1993. Contrary to the large-scale analysis, no significant relationship is found in this detailed study. However, a trend of dampened population growth right after the flood followed by an accelerated growth a decade later could be identified in the raw data and linked to explanations found in the literature.